What is hashing sounds like a simple question. It isn’t. Hashing sits at the center of modern computing. It protects passwords. It powers data structures. It keeps blockchains running. It verifies files. It helps systems run fast and stay secure.
People meet hashing in many places. Cyber security. Data structures. Java. Cryptography. Interviews. Exams. Real systems. The same word appears everywhere, yet the meaning shifts slightly by context.
This long guide explains hashing from the ground up. You’ll learn what hashing is, how hashing works, hashing techniques, hashing algorithms, how hashing is used, hashing in cyber security, hashing in data structures, hashing in Java, hashing in cryptography, advantages of hashing, and how hashing differs from encryption.
What Is Hashing
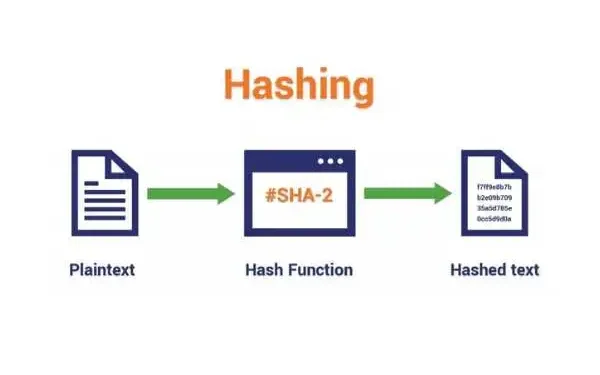
Hashing is the process of converting input data of any size into a fixed-size output called a hash value or hash code.
The input can be:
- a password
- a file
- a number
- a text string
The output:
- has a fixed length
- looks random
- represents the original data
A key point matters here. Hashing is one-way. You cannot reconstruct the original input from the hash.
Also Read : – Aesthetic Fonts in Canva: The Only Guide You’ll Ever Need
What Is a Hashing Function
A hashing function is the algorithm that performs hashing. It takes input data and produces a hash value.
A good hashing function:
- runs fast
- spreads values evenly
- gives the same output for the same input
- changes output completely if input changes slightly
That last property is called the avalanche effect.
How Does Hashing Work
Basic Working of Hashing
To understand how does hashing work, imagine this flow:
- Input data enters the hashing function
- The function processes the data mathematically
- A fixed-size hash value is produced
The same input always produces the same hash. A tiny input change produces a very different hash.
This behavior makes hashing reliable for comparison and verification.
Example of Hashing
Take a simple word like hello.
- Input: hello
- Hash output: a long string of letters and numbers
Change the input to Hello.
- Output changes completely
The hashing function treats inputs as raw data, not meaning.
What Is Hashing Technique
A hashing technique refers to the strategy used to store, retrieve, or protect data using hash values.
Different contexts use different techniques:
- data storage uses hashing for fast lookup
- security uses hashing for protection
- networking uses hashing for integrity
The core idea stays the same. Data turns into a fixed-size representation.
Hashing Algorithms
Hashing algorithms define how hashing functions operate. Some focus on speed. Others focus on security.
Also Read : – Amazing Apps For Amazon Fire Stick
Common Non-Cryptographic Hashing Algorithms
These algorithms focus on performance.
Examples include:
- MurmurHash
- CityHash
- Fowler–Noll–Vo (FNV)
They are common in databases and data structures.
Common Cryptographic Hashing Algorithms
These algorithms focus on security.
Examples include:
- MD5 (now insecure)
- SHA-1 (no longer trusted)
- SHA-256
- SHA-3
These are used where integrity and security matter.
What Is Hashing in Data Structure
What is hashing in data structure is a classic exam topic.
In data structures, hashing maps keys to positions in a data structure called a hash table.
The goal:
- fast insertion
- fast deletion
- fast lookup
Hashing allows average-case constant time operations.
Hash Table Explained
A hash table stores data as key–value pairs.
Process:
- Key passes through a hashing function
- Hash value determines index
- Value is stored at that index
This design avoids scanning the entire data set.
Collision in Hashing
A collision occurs when two different inputs produce the same hash value.
Collisions cannot be avoided completely. They can be managed.
Collision Resolution Techniques
Common methods include:
- chaining
- open addressing
- linear probing
- quadratic probing
Good hashing design reduces collision frequency.
What Is Hashing in DSA
What is hashing in DSA focuses on efficiency.
Hashing improves:
- search time
- insertion speed
- deletion speed
That is why hashing appears in almost every competitive programming problem set.
Also Read : – Deleting Apps On IPhone
Advantages of Hashing in Data Structures
Key advantages include:
- fast access
- scalable storage
- simple logic
- wide use cases
Hashing works well when data volume grows.
What Is Hashing in Cyber Security
What is hashing in cyber security shifts the focus from speed to protection.
In security, hashing protects sensitive data like passwords and files.
The goal:
- store data safely
- verify integrity
- prevent data recovery
Hashing helps even if systems are compromised.
Password Hashing Explained
Systems never store plain passwords. They store hashes.
Process:
- User enters password
- Password is hashed
- Hash is stored
- Login hashes input again
- Hashes are compared
The original password is never saved.
Salting in Hashing
Salting adds random data to input before hashing.
This prevents attackers from using precomputed tables.
Salt:
- is unique per user
- is stored openly
- increases attack difficulty
Modern systems always use salting.
Also Read : – Compass Apps for IPhone : Know About The Best Compass Apps For Your IPhone
What Is Hashing in Cryptography
What is hashing in cryptography deals with trust and integrity.
Cryptographic hashing ensures:
- data has not changed
- messages are authentic
- digital signatures remain valid
Hashing forms the backbone of many cryptographic systems.
Hashing and Digital Signatures
Digital signatures work like this:
- Data is hashed
- Hash is signed with a private key
- Receiver verifies using public key
Only the hash is signed, not the full data.
Hashing in Blockchain
Blockchains rely heavily on hashing.
Uses include:
- linking blocks
- verifying transactions
- securing consensus
Changing one block breaks the entire chain.
What Is Hashing in Java
What is hashing in Java usually refers to collections like HashMap and HashSet.
Java uses hashing to:
- store objects
- retrieve values quickly
- manage large data sets
Objects rely on hashCode() and equals() methods.
HashCode and Equals in Java
Java hashing depends on rules:
- equal objects must have equal hash codes
- unequal objects can share hash codes
Breaking these rules causes incorrect behavior.
Also Read : – 10 Best Apps for Aesthetic Edits to Transform Your Photos and Videos
What Is Hashing Function in Programming
In programming, a hashing function maps keys to indices.
Good hashing functions:
- distribute keys evenly
- avoid clustering
- reduce collisions
Choice of function affects performance.
How Is Hashing Used
How is hashing used depends on the system.
Common uses include:
- password storage
- file integrity checks
- database indexing
- caching
- load balancing
Hashing appears more often than most people realize.
Hashing vs Encryption
Hashing vs. encryption causes frequent confusion.
Hashing
- one-way process
- cannot recover original data
- used for verification
Encryption
- two-way process
- data can be decrypted
- used for confidentiality
Hashing protects integrity. Encryption protects secrecy.
Hashing vs Encoding
Another common mix-up.
- hashing secures data
- encoding changes format
- encoding is reversible
Base64 is encoding, not hashing.
What Is Hashing and What Are Its Advantages
What is hashing and what are its advantages can be summarized clearly.
Advantages include:
- fast data access
- secure password storage
- integrity verification
- efficient memory use
- scalability
These advantages explain its widespread use.
Limitations of Hashing
Hashing has limits.
Challenges include:
- collisions
- poor hash function choice
- brute-force attacks on weak hashes
Good design mitigates these risks.
Choosing the Right Hashing Algorithm
Choice depends on purpose.
- data structures need speed
- security needs strong cryptographic hashes
- file checks need consistency
No single algorithm fits all needs.
Real-World Hashing Example
When you download a file, sites provide a checksum.
You:
- hash the downloaded file
- compare it with published hash
Matching hashes confirm file integrity.
Hashing in Distributed Systems
Distributed systems use hashing for:
- consistent hashing
- load distribution
- fault tolerance
This keeps systems balanced and scalable.
Hashing and Performance
Hashing improves performance when designed well.
Poor hashing:
- increases collisions
- slows systems
- wastes memory
Design quality matters.
Also Read : – Best Camera App for iPhone: Know About These Amazing Photography Apps
Common Hashing Mistakes
Mistakes include:
- storing plain hashes without salt
- using weak algorithms
- ignoring collision handling
- assuming hashes are unique
Awareness prevents these errors.
Why Hashing Still Matters
Hashing remains essential in modern systems.
Cloud services. Security tools. Databases. Blockchains. All rely on hashing.
Understanding hashing improves system design and security awareness.
Also Read : – What Is The Enterprise Platform and How Does It Function?
Final Thoughts on What Is Hashing
Hashing turns data into a fixed-size fingerprint. That simple idea supports some of the most critical systems in computing. From protecting passwords to speeding up data access, hashing works quietly in the background.
Learning hashing means learning how trust, speed, and structure come together in software systems.
FAQs: What Is Hashing
What is hashing
It converts data into a fixed-size hash value.
How does hashing work
Input passes through a hashing function to produce a unique-looking output.
What is hashing in data structure
It maps keys to positions for fast access.
What is hashing in cyber security
It protects passwords and verifies data integrity.
Hashing vs encryption
Hashing is one-way. Encryption is reversible.
What is hashing in Java
It supports collections like HashMap using hashCode values.